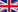
In this section of VLab gas turbine operation study is performed with the aid of computer models. Introducing the principles of operation this way has two purposes: (a) to explain how the gas turbine works and behaves, (b) to give the basics of building a model. The included models represent a number of specific engines that are used in Greek air and navy force. This helps the students of air and naval force academy to come in contact with the engines that are going to work with in their subsequent career.
 Main Screen of 'Study of Operation' Section
Main Screen of 'Study of Operation' Section
For each one of the selected engines detailed technical information is presented in the form of web pages. A computer model for estimation of gas turbine operation and performance using the TEACHES software package has been created and included in VLab. The incorporated models use the same interface and thus the students can be easily familiar with them and understand their functionalities.
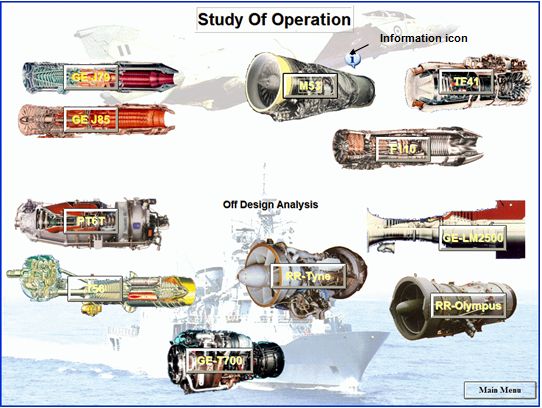
 Main Screen of Gas Turbine Performance Simulator
Main Screen of Gas Turbine Performance Simulator
The visual interface of the incorporated simulation programs is designed to perform the following functions:
- Contain the variables associated with engine performance grouped in three different kinds: (a) operating point parameters (input), (b) component health parameters (input), (c) performance parameters (output).
- Contain a visual impression (picture) of the actual engine. An axial engine cutout is considered to be a good choice.
- Contain some space available for graphic representation of the most important performance related information.
In addition to this basic information different groups of functions are given in the form of menus. After a calculation is completed, the main quantities of interest are displayed on an engine cutout. This type of display gives a feeling of what changes take place in the engine by showing local quantities, such as temperatures, in relation to their actual mechanical location on the engine. The user can also visually examine overall performances or variation of specific quantities for different operating conditions in corresponding graphs. For example the dependence of twin shaft engine load on ambient temperature for operation with constant turbine inlet temperature can be immediately seen.
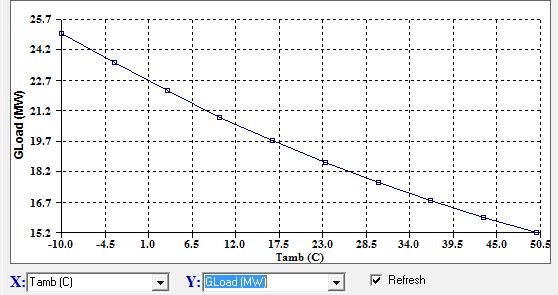 Engine Load vs Ambient Temperature for constant TIT
Engine Load vs Ambient Temperature for constant TIT
Another significant feature of this software is the possibility it offers to understand the effects of malfunctions through the simulation of component faults. Such faults are simulated by modification of the performance characteristics of the components.